问题
最优化理论与算法课程作业题,用遗传算法求解如下问题:
$$
max \quad f(x) = x \cdot sin(3x) , -1 \le x \le 30
$$
算法思路
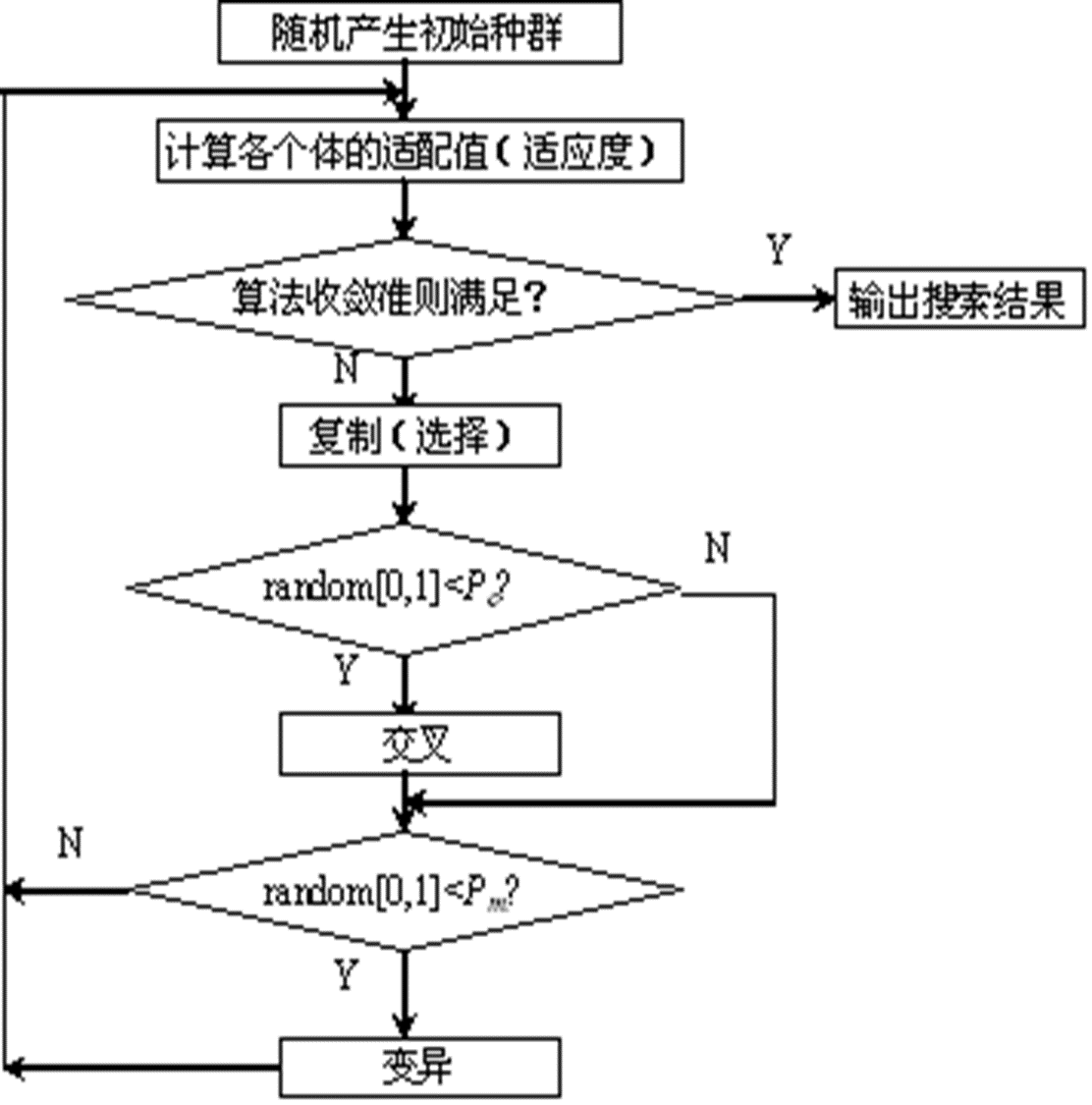
算法基本流程资料已经很多了,这里贴一个课程PPT里的图:
编码
将问题的解用一种码表示,常用二进制编码。
此题中解即为x的值,考虑6位小数精度,将区间$[-1,30]$调整位$[0,31\cdot 10^{6}]$,得到二进制码码长为25,即基因长度。
基因编码和实际解转换如下:
$$
x = lower+x_{dec}\cdot \frac{upper\ - lower}{2^{genelength}-1} \\
x_{dec} = bin2dec(x_{bin})
$$
产生初始种群
确定好了编码类型和长度之后,产生初始种群,选择合适的种群大小。
1
2
| % 初始化种群
populations = randi([0, 1], population_size, gene_length);
|
计算适应度
遗传算法中以种群中个体的适应度来作为选择的依据。本题中适应度由目标函数变换而成。
$$
fitness(x) = f(x)
$$
适应度计算函数:cal_fitness()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| % 计算适应度函数
function fitness = cal_fitness(func, populations, upper_limit, lower_limit)
[population_size, gene_length] = size(populations);
populations_x = bin2dec(num2str(populations));
x = lower_limit + populations_x * (upper_limit - lower_limit) / (2 ^ gene_length - 1);
fitness = zeros(population_size, 1);
for i = 1:population_size
fitness(i) = func(x(i));
end
end
|
选择
得到种群中个体的适应度后,便可以根据适应度进行选择。常用的选择方法为:比例选择。其基本思想:每个个体被选中的概率与其适应度值成正比,设种群规模为$M$,个体$i$的适应度值为$f_i$,则个体$i$被选中的概率$P_i$为:
$$
P_i = \frac{f_i}{\sum_{i = 1}^{M}f_i}
$$
确定好选中概率后,采用轮盘赌的方式来选择出个体。轮盘赌次数为个体数量。
轮盘赌选择函数:select_population()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| % 计算适应度函数
function fitness = cal_fitness(func, populations, upper_limit, lower_limit)
[population_size, gene_length] = size(populations);
populations_x = bin2dec(num2str(populations));
x = lower_limit + populations_x * (upper_limit - lower_limit) / (2 ^ gene_length - 1);
fitness = zeros(population_size, 1);
for i = 1:population_size
fitness(i) = func(x(i));
end
end
|
交叉
选择出个体后,根据交叉概率,对个体进行两两交叉操作,对于二进制编码,常用交叉的方法是单点交叉。交叉概率用以决定当前一对个体是否进行交叉,不宜太大,否则个体更新过快,高适应度的个体容易被破坏,不宜太小,否则算法容易停滞。
交叉函数:cross_population()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| % 交叉
function new_populations = cross_population(populations, cross_prob)
[population_size, gene_length] = size(populations);
new_populations = populations;
for i = 1:2:population_size
prob = rand; % 用于判决是否进行交叉
if prob <= cross_prob
cross_index = randi([1, gene_length]);
temp = new_populations(i, :);
temp(:, cross_index:end) = new_populations(i + 1, cross_index:end);
new_populations(i + 1, cross_index:end) = new_populations(i, cross_index:end);
new_populations(i, :) = temp;
end
end
end
|
变异
交叉完成后,根据变异概率对个体进行变异操作,具体是指对变异的个体随机选择某一位进行反转操作。并非所有被选择的个体,都要进行变异操作。变异概率太小很难产生新个体,太大会使GA成为随机搜索。
变异函数:mutate_population()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| % 变异函数
function new_populations = mutate_population(populations, mutation_prob)
[population_size, gene_length] = size(populations);
new_populations = populations;
for i = 1:population_size
prob = rand; % 决定是否变异
if prob <= mutation_prob
mutation_index = randi([1, gene_length]);
new_populations(i, mutation_index) = ~new_populations(i, mutation_index);
end
end
end
|
算法终止判断
常用预先设定迭代(进化)次数作为终止条件。其次以最优值是否连续若干步没有明显变化作为终止条件。
主函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| clear;
clc;
close all;
% 目标函数
func = @(x) x * sin(3 * x);
% 全局参数
population_size = 100; % 种群数量
gene_length = 25; % 基因长度,精度定为6位小数
cross_prob = 0.20; % 交叉概率
mutation_prob = 0.01; % 变异概率
max_epochs = 1000; % 最大迭代次数
upper_limit = 30; % 上限
lower_limit = -1; % 下限
best_x_bin = []; % 最优解
best_f = -Inf; % 最优解适应度
% 初始化种群
populations = randi([0, 1], population_size, gene_length);
% 迭代主函数
for epoch = 1:max_epochs
% 计算适应度
fitness = cal_fitness(func, populations, upper_limit, lower_limit);
% 选择 轮盘赌
populations_selected = select_population(populations, fitness);
% 交叉
populations_crossed = cross_population(populations_selected, cross_prob);
% 变异
populations_mutated = mutate_population(populations_crossed, mutation_prob);
% 更新种群
populations = populations_mutated;
% 更新最优解
fitness = cal_fitness(func, populations, upper_limit, lower_limit);
[max_fitness, max_index] = max(fitness);
if max_fitness > best_f
best_x_bin = populations(max_index, :);
best_x = bin2dec(num2str(best_x_bin));
best_x = lower_limit + best_x * (upper_limit - lower_limit) / (2 ^ gene_length - 1);
best_f = max_fitness;
end
end
|
结果
1
| 最优解 x = 29.840208, 目标函数值 f = 29.836955
|
